Understanding Gum Disease: Prevention, Symptoms, and Treatment Options
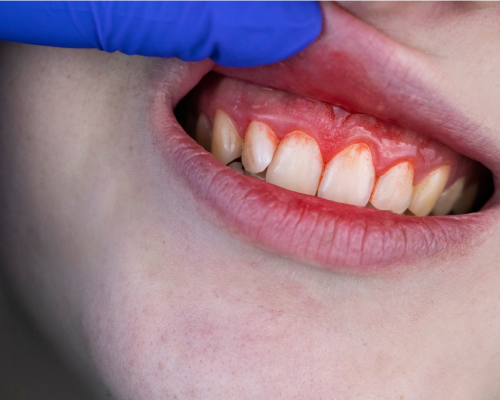
Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common yet serious condition that affects the health of your gums and the bones supporting your teeth. If left untreated, gum disease can lead to tooth loss and other significant health problems. In this blog, we’ll explore the stages of gum disease, how to recognize the symptoms, and what you can do to prevent and treat it.
The Stages of Gum Disease:
- Gingivitis: Gingivitis is the earliest stage of gum disease, characterized by inflammation of the gums. It is often caused by a buildup of plaque on the teeth. Symptoms may include red, swollen gums that bleed easily during brushing or flossing. Fortunately, gingivitis is reversible with good oral hygiene and professional cleaning.
- Periodontitis: If gingivitis is not treated, it can progress to periodontitis, a more severe form of gum disease. In periodontitis, the inner layer of the gums pulls away from the teeth, forming pockets that can become infected. The body’s immune response to the infection can result in the breakdown of bone and connective tissue, potentially leading to tooth loss.
- Advanced Periodontitis: In the advanced stage of periodontitis, the bone and fibers supporting your teeth are destroyed, which can cause teeth to shift or loosen. This can severely affect your bite and may lead to the need for teeth to be removed.
Symptoms to Watch For:
- Bleeding Gums: Gums that bleed during brushing or flossing are often one of the first signs of gum disease.
- Persistent Bad Breath: Bad breath that doesn’t go away after brushing can indicate the presence of bacteria and gum disease.
- Receding Gums: Gums that appear to be pulling away from the teeth, making the teeth look longer, can be a sign of periodontitis.
- Loose Teeth: As gum disease progresses, it can weaken the support structures of your teeth, leading to mobility or tooth loss.
Prevention and Treatment:
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Brush your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and floss daily to remove plaque from between the teeth and under the gumline.
- Regular Dental Visits: Regular checkups and professional cleanings can help prevent gum disease and detect it early when treatment is most effective.
- Professional Treatment: If you are diagnosed with gum disease, your dentist may recommend a deep cleaning procedure called scaling and root planing to remove plaque and tartar from above and below the gumline. In more severe cases, surgical interventions such as flap surgery or bone grafting may be necessary.
Conclusion: Gum disease is a serious condition that can have lasting effects on your oral and overall health. By understanding the stages, recognizing the symptoms, and taking preventive measures, you can protect your gums and maintain a healthy smile. Don’t wait for symptoms to appear—schedule regular dental visits to catch and treat gum disease early.